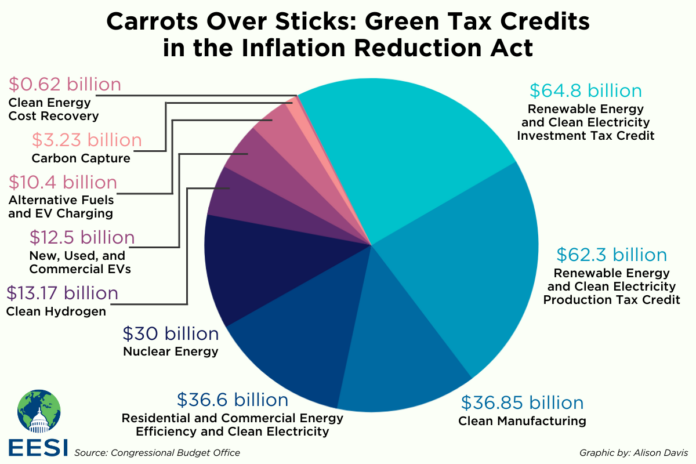
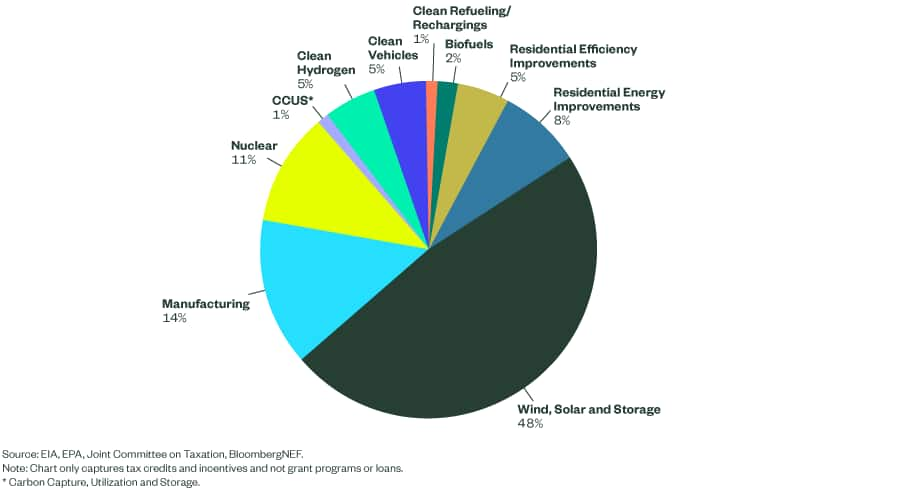
In this article, we will explore the impact of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) on clean energy projects. With $400 billion in federal funding allocated towards clean energy initiatives, the IRA has paved the way for an increase in private investment in climate tech startups. Over the past year, more than 270 new clean energy projects have been announced, with a staggering $132 billion in private investments. These funds are largely directed towards areas such as electric vehicles, batteries, renewable energy, grid storage, carbon capture and utilization, clean fuels, and more. The IRA has not only led to an upsurge in climate-related startups but has also empowered their customers by offering incentives that enable them to sell their products. Furthermore, the IRA has improved access to debt financing at the growth stage, particularly for domestic manufacturing and clean energy projects. From solar and energy storage to hydrogen and EV manufacturing, the IRA’s impact on various sectors of the clean energy industry is significant. Additionally, the act extends tax credits, supports clean hydrogen fuel and biofuels, and boosts the valuation of startups involved in carbon capture and sequestration. With the emergence of new business sectors and expectations of significant private capital investment, the IRA is set to shape the future of clean energy.
Summary
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) has made a significant impact on the clean energy sector, allocating $400 billion in federal dollars for clean energy projects. This massive funding has driven private investment in climate tech startups, with total private investments reaching approximately $132 billion. More than 270 new clean energy projects have been announced in the past year, focusing on various areas such as EVs, batteries, renewable energy, grid storage, carbon capture, utilization and storage, and clean fuels. The IRA has also spurred a 10% increase in climate-related startups since its implementation. This article will delve into the specific effects of the IRA, highlighting its impact on private investment, debt financing, tax credits, startup sectors, and emerging business sectors.
1. Overview of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA)
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is a significant piece of legislation that aims to combat inflation and promote economic growth. One of its key provisions is the allocation of $400 billion in federal funds for clean energy projects. This substantial amount will enable the implementation of numerous initiatives, including the development of clean technologies, the modernization of infrastructure, and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The overarching objective of the IRA is to support the transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy system.
2. Impact on Private Investment in Clean Energy Startups
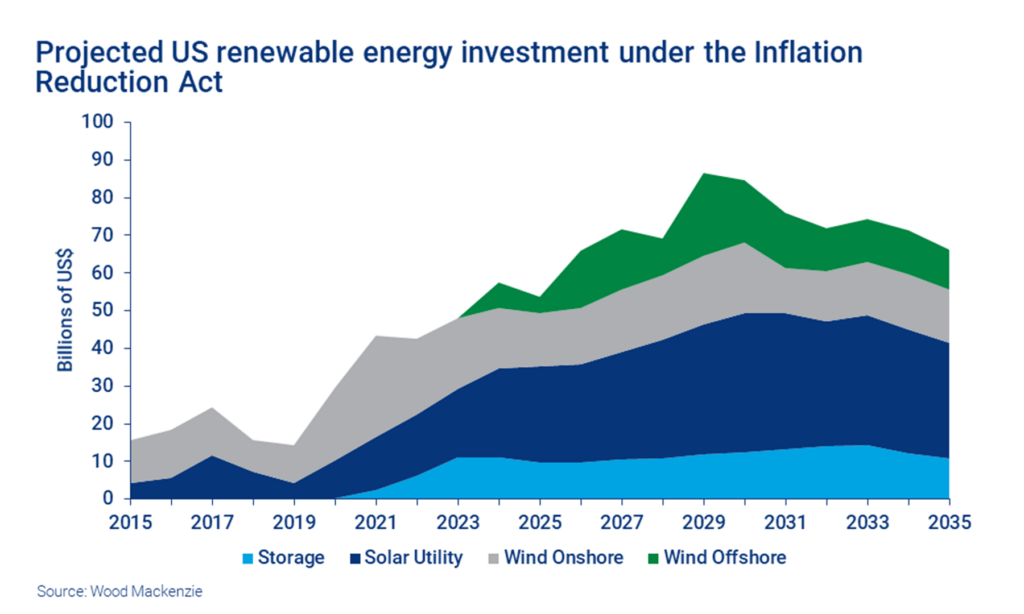
The IRA has played a pivotal role in driving private investment in climate tech startups. With the promise of federal funding, private investors have recognized the immense potential for growth and innovation in the clean energy sector. The total private investments in clean energy projects have reached an impressive $132 billion, indicating a significant influx of capital into startups focused on sustainable technologies. This surge in private investment has fueled the development of more than 270 new clean energy projects in the past year, fostering entrepreneurship and driving economic growth.
Private funds are primarily channeled towards key sectors such as electric vehicles (EVs), batteries, renewable energy, grid storage, carbon capture, utilization and storage, and clean fuels. These sectors are at the forefront of the clean energy revolution, and private investors see immense potential for profit and societal impact. Startups across all stages, from early-stage ventures to more mature companies, have benefitted from the increased private investment. Since the signing of the IRA, there has been a notable 10% increase in the number of climate-related startups.
Moreover, the IRA’s funding has had a direct and positive impact on startups’ customers. The incentives provided by the bill enable startups to sell their products and services at more competitive prices, making clean energy solutions more accessible to a wider range of consumers. This not only benefits the startups themselves but also drives the overall adoption of clean energy technologies.
3. Access to Debt Financing and Incentives for Clean Energy Projects
In addition to private investment, the IRA has enhanced access to debt financing, particularly at the growth stage. Startups engaged in domestic manufacturing and clean energy projects now have increased opportunities to secure financing for expansion and research and development. The availability of debt financing further accelerates the development and deployment of clean energy technologies, enabling startups to scale their operations more rapidly.
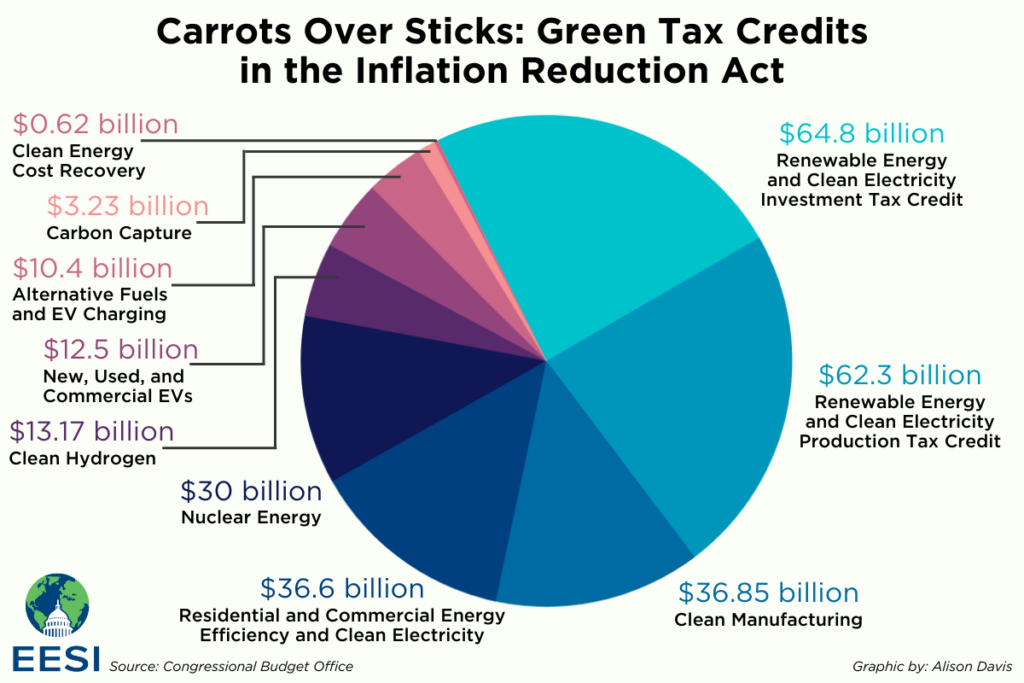
The IRA also provides several incentives to support clean energy projects. These incentives include tax credits, loans, and grants that aim to encourage the adoption and development of sustainable technologies. Startups can benefit from tax credits for various activities, such as solar installations and the construction of energy storage systems. The loans offered under the IRA enable the construction and modification of generation and transmission facilities, improving grid reliability and facilitating energy sharing across different regions. These incentives not only provide support at critical stages of a startup’s growth but also contribute to the overall advancement of the clean energy sector.
4. Impact on Specific Startup Sectors
The IRA’s provisions have had a profound impact on specific startup sectors within the clean energy industry. The solar sector, for example, has seen significant benefits from the IRA. The extension of tax credits for solar installations has incentivized the deployment of solar energy systems, resulting in increased demand and market opportunities for solar startups. Additionally, the inclusion of standalone energy storage systems for tax credits has further boosted the growth of startups specializing in energy storage technologies, addressing the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
The energy transmission sector has also experienced positive effects from the IRA. The loans provided by the Act support the construction and modification of generation and transmission facilities. This investment in grid infrastructure improves reliability and enables efficient energy sharing across regions, benefiting startups involved in energy transmission technologies.
The IRA has also provided a boost to the hydrogen sector. Tax credits have been extended to support clean hydrogen fuel, encouraging startups to invest in research and development to advance hydrogen production and utilization technologies. Similarly, tax credits for biofuels and sustainable aviation fuel have created opportunities for startups in these sectors.
Carbon capture and sequestration startups have witnessed a boost in valuations since the IRA’s passing. The Act’s focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting carbon capture technologies has attracted significant investments, enabling startups to develop and commercialize their innovative solutions.
The IRA’s tax credits have particularly driven investments in domestic EV manufacturing and the EV supply chain. The incentives provided by the Act have catalyzed the growth of startups involved in electric vehicle production and related infrastructure, creating jobs and contributing to the expansion of the clean transportation sector.
5. Extension of Tax Credits and Support for Clean Energy Technologies
One of the notable provisions of the IRA is the extension of tax credits for solar installations. This extension has incentivized the adoption of solar energy systems, promoting the use of renewable energy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Startups specializing in solar technologies have taken advantage of these tax credits, resulting in increased installations and market opportunities.
Furthermore, the inclusion of standalone energy storage systems for tax credits has greatly encouraged the development and deployment of energy storage technologies. Energy storage is essential for enabling the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid, and the IRA’s support has bolstered the growth of startups in this sector.
The IRA also provides loans for the construction and modification of generation and transmission facilities. This financial support enhances grid reliability and facilitates energy sharing between different regions, promoting efficient and sustainable energy distribution. Startups involved in energy transmission technologies have been able to leverage these loans to expand their operations and contribute to the improvement of the overall energy infrastructure.
Additionally, the IRA includes tax credits to support clean hydrogen fuel, biofuels, and sustainable aviation fuel. These tax credits have created an environment conducive to innovation and investment in these areas, allowing startups to develop and commercialize technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable energy alternatives.
6. Boost in Valuations and Investments
The passing of the IRA has resulted in a notable boost in startup valuations within the carbon capture and sequestration sector. The Act’s focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions has attracted significant investments to startups working on carbon capture technologies. These technologies aim to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions, mitigating the impact of industrial processes and reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The increased valuation and investment in these startups reflect the growing recognition of the importance of carbon capture in addressing climate change.
Similarly, domestic EV manufacturing and the EV supply chain have witnessed significant investments due to the IRA’s tax credits. The Act’s focus on supporting electric vehicles has spurred the growth of startups involved in the production of EVs and the development of related infrastructure. This investment has enabled startups to expand their operations, create jobs, and contribute to the transition to cleaner transportation options.
7. Impact on the EV Charging Industry
The IRA’s tax credits have also had implications for the EV charging industry, although the impact has been mixed. Tax credits are available for EV charger installations, incentivizing the development of charging infrastructure. However, there have been varying outcomes in terms of the industry’s growth. While some startups in the EV charging sector have thrived, others have faced challenges, particularly in highly competitive markets. Nonetheless, the availability of tax credits has undoubtedly contributed to the overall expansion of the EV charging industry and the accessibility of electric vehicle charging options.
8. Emergence of New Business Sectors
The implementation of the IRA has led to the emergence of new business sectors that support the clean energy industry. One such sector includes startups that help businesses understand the tax code related to clean energy investments. With the introduction of new incentives and tax credits under the IRA, many businesses may require assistance in navigating the complex tax regulations. Startups specializing in tax consulting and advisory services have emerged to fulfill this need, providing guidance and expertise to businesses aiming to take advantage of the available incentives.
Additionally, the IRA has fostered the creation of marketplaces for transferable tax credits. Some startups have established platforms that facilitate the trading and utilization of tax credits related to clean energy investments. By connecting businesses with excess tax credits to those who can benefit from them, these marketplaces promote greater utilization of available incentives, maximizing the impact of the IRA’s provisions.
9. Expectations of Private Capital Investment
The investment provided by the IRA is not considered overhyped, as there are high expectations of significant private capital investment in the clean energy sector. The IRA’s allocation of $400 billion in federal funds for clean energy projects has acted as a catalyst, attracting private investors and driving the growth of climate tech startups. The positive momentum generated by the IRA is expected to continue, with private capital investment playing a crucial role in further advancing sustainable technologies and driving the clean energy transition.
In conclusion, the Inflation Reduction Act has had a transformative impact on the clean energy industry. Through its allocation of federal funds, the IRA has encouraged private investment, expanded access to debt financing, extended tax credits, and supported various startup sectors. The Act has not only boosted startup valuations but also driven innovation, job creation, and the emergence of new business sectors. With expectations of significant private capital investment, the IRA has laid the foundation for a more sustainable future and a thriving clean energy sector.